12 Feed the Planet (Knaple)
Feed The Planet (FTP)
People are fighting all over the Planet to meet basic needs, so we must Feed The Planet.
Feed the Planet is a project and vision to engage needed communication with scientists, security experts, military, religious people, and global leaders to convene solutions to sustain us during war and peace. One must return to the basics to sustain life and end worldwide hunger and suffering. Advancing technologies for humanity will help with food, water, and shelter to help make life truly flourish. FTP expands upon previous work through the Kumasi Institute of Tropical Agriculture (KITA) in Ghana[1] (Mirani, 2018) and the Worldchefs Organization[2] (UN: Department of Economic and Social Affairs- Sustainable Development, 2024) by using the power of the Internet, smart villages, intelligent chain management, wind and solar energy, automated parks, school-in-the-box, lab-in-the-box, and drones for EMT. The author presents a beautiful vision of applying advanced technologies for humanitarian purposes.
During times of war or peace, outside-of-the-box solutions need to be implemented for society and, most importantly, children to succeed. Wars are usually fought over resources. Food and water scarcity issues are one of the leading causes of death globally. A plan is needed so society will not keep repeating the mistakes of our past. The breadbasket of Europe and the amber waves of grain in America are running low at the wrong time. COVID and war have challenged society. Now, it is time for solutions.
The Feed the Planet project envisions land development in multiple African locations and other locales throughout the Planet. Developing Economic Development Zones, MOAs, and regulatory compliance measures will help protect people and global investments. Defensive and offensive capabilities will be integrated to help establish the rule of law in these zones. Technology will help define laws in overlapping jurisdictions. Jurisprudence measures will be fast, accurate, and uniform across the board.
Feed the Planet is envisioned as a global project. The main goal will be to use organic farming techniques as much as possible to increase food production. Feed the Planet envisions the development of land use as needs arise. Certain countries have a greater abundance of resources than others. GMO crops, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides will be used in specific locations. FTP starts the revolution in the Itombwe Mountains in Africa.
The Itombwe Mountains have a section 1000 km long and 18 subterranean minerals that can be used for multiple-use farming. If the initial FTP project succeeds, other areas in Africa, Asia, and elsewhere can be developed according to the Intombwe hanging organic farming model.
A global development project allows us to use the resources as a whole through a systems lens of sustainable development. UN, Governments, NGOs, and individuals involved in humanitarian efforts will be required to develop a plan for refugees and immigration during wartime or militia activity. [3]
The Feed the Planet project was designed with the knowledge that a contingency plan was needed to help BRICS and Allied countries collaborate on humanitarian goals during a state of war. The UN is not as well received in some countries as others. This does not help fill a needed gap in communication to foster cooperation on global goals.
Hanging Gardens of Africa
The DRC,[4] the Republic of the Congo, and some other regions have vast amounts of wheat that can be used for organic gardening. Out of all the resources of the Great Continent, the 16 feet of peat is the most incredible.
![Artist sketch of Hanging Gardens concept /The DRC,[4] the Republic of the Congo, and some other regions have vast amounts of peat that can be used for organic gardening. Out of all the resources of the Great Continent, the 16 feet of peat is the most incredible.](https://kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub/app/uploads/sites/77/2024/06/Figure-12-1-Hanging-Gardens-of-Africa-Sketch-300x190.png)
FTP will build a vertical agricultural infrastructure to pull that great peat upwards and produce organic goodness to feed the masses. Instead of just using that top foot of peat, [5] FTP will use the 15 feet underneath. Horizontal farming works, but other options exist to maximize the resource sustainably. Sometimes called the Cuvette Centrale, this peatland covers 145,529 square kilometers (56,189 square miles) in the northern Republic of Congo and the Democratic Republic of Congo and holds about 20 times as much carbon as the US releases from burning fossil fuels in a year. (Wikipedia, 2024)
The Itombwe Mountains’ biodiversity is incredible, and they probably have some peat bog areas, unlike the two Congo regions mentioned above. Peat can be mixed with compost, topsoil, and sand to make the most incredible growing medium. Different plants need slightly different mixes to flourish.
Hanging Gardens Magic
One can suspend soil by using simple steel cabling, tree trimming(upcut), drilling through the tree, anchoring, and pulling a cable run to another tree or anchoring spot(rock). This can be anchored easily into river valleys with good rock. Dynamic climbing rope sections are suspended on selected spots along the cable, and a carousel (round) holds approximately ten pulleys for plants. Each pulley would hold approximately ten plants, and a carousel could be placed at the bottom to ensure better structural integrity. A dynamic rope would drop between the middle so climbers can ascend to care for plants. Depending on the plants, we can wrap a material, Visqueen or similar, around the carousel to create a greenhouse effect. Mesh holders can be used like pots or with pots to suspend the plants on a static rope used with the pulleys.
The process can be fully automated or use available labor to keep it simple. Once the vertical infrastructure is built, the main thing would be to keep the supply chain running. Water lines can be gravity-fed or pneumatic-driven. The FTP project will integrate automated farming techniques, and IoT will connect the sensors, cameras, and people. Sensors can be attached to monitor pH and moisture, and equipment like cameras can be used.
The FTP project will integrate automated farming techniques, and IoT will connect the sensors, cameras, and people. Human Machine Interface (HMI) is now in peoples’ hands. Phones can track crops and investments and even order supplies with an inventory tracking system built in. Water can be sprayed directly on plants with a drone. This saves money from targeted spraying techniques.
Bringing it off the ground vertically, FTP does not have to deal with as many pests. The drones will help identify infestations, monitor overall plant health quickly, and then decide if areas need to be sprayed. Care must be taken to avoid losing the organic rating using pesticides. Spraying organic solutions is the solution. Just because the solution is organic does not mean it is not harmful.
In other areas that will be developed, where the soil is depleted, a balance of organic and chemical applications based on crop, climate, and location can be used. Even in organic farming, chemical pesticides can be used under certain conditions. No natural alternative exists that can effectively target the same plant diseases as copper sulfate.
With AI swarm technology, FTP can have flying drones harvesting genetic information from plants, birds, and animals. Each Bee (Drone) can communicate with the swarms to canvass an area and provide valuable information. (Nichols & al., 2019) (Nichols R. -2., 2022)
As FTP develops this soil, it also processes minerals in these regions. FTP could take soil core samples to establish land according to potential and market needs. Soil core samples can be harvested by bigger drones and brought back to the central lab for identification. FTP will be canvassing an area the size of the Appalachian Trail with just the Itombwe Mountains. Smart Villages can be moved with helicopters and dropped into regions cleared for development. Road building could invite encroachment into the development zone. Therefore, road infrastructure would not be needed in all areas. Sensors would be all over the jungle to alert of possible dangerous situations. Geospatial capabilities have been recently upgraded. OSINT and other forms of intelligence are needed to keep people and investments safe.
Smart Supply Chain
The use of robotics, drones, and automation in warehouses and distribution centers will continue to grow. Companies have implemented Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) to optimize operations and reduce labor costs. Feed The Planet will use AI to control the movements of its UAVs to harvest vegetables, grains, and minerals in mining operations.
The UAVs will drop totes, or bins, at a satellite center and later be brought to a central warehouse or staging area for shipment. This will help cut down the time involved in getting organic vegetables from farm to fork. This will help cut down the time involved in getting organic vegetables from farm to fork. In organic farming, some of the food loss comes from the time involved with supply chain pain points. AI and data analytics are revolutionizing logistics and agriculture. These technologies enable better demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and route planning. Predictive analytics and machine learning are helping companies, governments, and individuals build a Smart Supply Chain to meet needs on a societal level. In order for humanity to succeed, we must learn from our mistakes, make informed decisions, and establish best practice procedures.
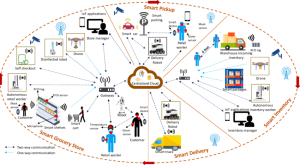
Vertical Solar and Wind Incorporated into FTP
FTP can incorporate solar panels right into the design with the Vertical Hanging Gardens infrastructure. The panels can be soldered right into the stainless-steel cabling. The vertical solar panels would be run at different heights on the tree and attached to a small motor. The small motor lets the cabling spin according to the sun’s position and inclement weather.
Lumen sensors can read the sun’s directional energy and rotate as the sun moves from east to west for maximum energy capture. Because of the sun’s cycle, even a simple timer can rotate the cabling for the panels. A barometric sensor can alert the system, even the village, of inclement weather. This will then sound an alarm and rotate the panels out of harm’s way.
Because of the sun’s cycle, we can hang the panels at different levels. Staggering panels at various levels (30 feet, 20 feet, and 10 feet) allows the panels to capture the most available light and still grow crops like broccoli underneath. Exciting discoveries are being made in the field of Agrivoltaics. Partial shade plants will still flourish, and this will help trap moisture at ground level in most situations. These panels can provide shade and cooling effects in the Smart Village to Smart City concept.
However, the most significant financial benefits for farmers come from producing energy. According to the study, solar energy was about ten times the income from broccoli, which indicates that farmers already growing the vegetable are missing out on an opportunity by not having solar panels in the same fields. (Gearino, 2022)
The vertical wind project will use anchors in similar locations and have a motor to pitch the wind turbines like the solar panels. The height will usually be about 10 meters(30 feet). This is the level that optimizes wind conditions in most circumstances. In river valleys, the continuum of energy generated by moving water gives some non-traditional harvesting locations for wind. Updrafts and downdrafts form in river valleys according to wind direction, sunlight conditions, and location within the river valley. The river meanders in different directions as it moves through the mountains. This gives different exposures and directions the wind can come from.
A drone will scout locations to decide where to suspend the wind turbine. The drone will be fitted with a wind velocity sensor. It will also have a windsock equipped with a camera pointed at it. This will tell how the wind turbine should be pitched to optimize wind direction. The most likely scenario is pitched upwards more at night and early morning from cold air settling. Around noon, it would be almost level. As the warm air rises, pointing the turbine towards the ground seems logical. This is a generalization for summertime conditions.
A drone with sensors can canvas large areas to optimize wind turbine position. The wind turbines in river valleys and mountain gorges can be suspended depending on the effects on the endemic bird population of land that was once thought of as unusable for agricultural use and can be used to harvest wind, solar, and food to help Feed the Planet.
Smart Village to Smart City
Feed the Planet (FTP) will use the Smart City Concept for its Smart Villages transitions. The Smart Village to Smart City is a 13-year development goal. The first three years are about picking suitable locations, securing and expanding the perimeter, and laying the essential infrastructure for some of the projects. Containers will be dropped at selected sites for medical supplies, learning, lab research, and other purposes. Starting in late 2027, decisions will be made about which sites will most likely succeed in completing the Smart City build.
The ideal location selection would be right along a river corridor or near a reliable water source. Hydraulic power sources would be available, enabling ways to design a septic and sewer system considering drain fields, sanitary, and stormwater run-off. As the village grows into a city, water would be diverted to other parts of the town by building gates upriver. Having canals and rivers run through the city will also increase recreational opportunities.
FTP will immediately start composting the organic material to enrich our soil and help with garbage build-up. Black Soldier Fly Larvae can help with sanitation, aquaponics, fish hatcheries, and other uses. Understanding what bugs can do for a city, river, and lake system is crucial for this project. The Itombwe Mountains are cold enough to support a trout population for food and recreational opportunities.
The Smart city should be laid out in a circular grid. Streets run east-west and then north-south. The east-west streets will have vertical solar, transportation, and utility plenum above ground(2nd floor) and e-bike infrastructure for every other block. This will allow energy collection and green zones for pleasure as well. North-south streets will have full transportation options about every 4th street.
Designing buildings to not compete with each other for light will be essential to creating a balanced city. The buildings will all be approximately 30 feet tall and will have four levels. The basement and three floors will be the universal build. Cities that touch the sides of the river canyon will be built higher into the cliff. Designing buildings to harvest the sun’s full potential will be necessary for growing food on the sides of buildings. Aquaculture can work well on the sides of the buildings depending on the crop grown.
Some ways to prevent creating urban heat islands are vegetation, shading from solar panels, aquaponic containers, and reflective materials. Airflow through cities and buildings will be discussed to understand ways to optimize positive and negative airflow. This natural ventilation of buildings depends on climate, building design, and human behavior. (Atkinson & al., 2009)
Urban planning will be a community event to empower the citizens. Informed citizens will help the community grow positively. Discussing where to have proteins like chicken coops, fowl, and fish farming in the community will help foster understanding.
The initial building will consider the medical infrastructure to achieve timely medical treatments. A 15-minute city in Europe received negative press when someone passed away from medical service failure. We will have a blank slate to build it right the first time. We will not have to retrofit an old city with new technologies. Energy development, battery storage for harvested energy, electrical grid considerations, heliports, and other solutions make this project ideally suited for open-source development. Project designs will not always be identical. Adjustments will be made according to location needs.
Automated Parks Project (APP)
FTP will model its vision to incorporate the APP. APP has been in development for over 20 years. The sight and sound regulation was expanded on in the Kenai River Guide Academy in 2021. RF senders and RF receivers can expand our capabilities to lower prices and help save lives. Drones fitted with cameras and RF senders and people with RF receivers can save lives and be used in rescue. When a passenger has a medical emergency and the guide cannot walk the passenger up to the road, a drone could fly with the passenger to ensure that the patient receives treatment from the EMT. Mounting cameras on drones, with RF senders and RF receivers, can save lives and be used in rescue operations by our federal agencies. It can be used to help calm families in emergencies by having a trained EMT 911 first responder handle the drone conversation with the affected party. (Odero, 2021)
School-in-a-box (SIAB)
FTP also envisions the SIAB concept. The first versions of school-in-a-box will have either solar, wind, generator, or hydraulic energy sources for computers and the data center. It will have satellite communication capabilities to source online learning tools for classroom instruction and training. Educational opportunities provide ways to encourage growth in a community. Including ICT and STEM learning material within the curriculum will enable students of all ages to succeed in an ever-changing work environment. (UNICEF, 2024)
In case of satellite system failure, a backup contingency plan with learning redundancy is in place with digital and on-premise libraries. The libraries will have both old and new textbooks as well as classic fiction and literature for Pre-K through college. The sciences will be well represented, including everything to do with aircraft and spacecraft, how to make them, and how to repair them.
The SPACE library project has added children’s books and textbooks as well as classic fiction and literature. (Powell, 2019) The sciences will be well represented, and everything has to do with aircraft or spacecraft – how to make them and how to repair them. This project will be built into a container for ease of shipment. One A2N carries computers and solar power systems, or alternative power, for computers with extra capacity. Another A2N carries books and eBook readers and possibly small laptops for children and education. This is just one example of how Smart Villages will be developed quickly and create an intelligent supply chain. Containers will be transported by helicopters or VTOL aircraft and airdropped into cleared areas. Each location will have custom solutions based on location specifications. Some will have five computers that run off solar in the day and lead batteries at night for up to 10 days, even without sunlight. Boots on the ground scouting for locations will aid in determining the best areas to build Smart Cities.
Lab-in-a-Box (LIAB)
FTP envisions incorporating the concept of Lab-in-a Box. (LIAB) Harvesting genetic information from plants, identifying endemic populations of birds and animals, and overall care of an environment can be enhanced with drone technology. Scientists can easily canvas large swatches of land with AI Swarming Drones and then communicate through a central or satellite lab. Working class drones, people, and automated vehicles will take soil core samples, measure mineral wealth with lidar, GPR, and utilization of geospatial capabilities, identify areas that have threatened populations of birds and animals, and modify automation techniques to engineer solutions as needed for drones and automated vehicles. (DATA SCIENCE, INDUSTRIES, 2023)
Soil core samples can be harvested by bigger drones with modified attachments using simple solutions like plastic tubing with a drill bit center to trap soil samples. This will now be brought back to the lab and analyzed for soil conditions and mineral wealth trapped in the growing medium. (DATA SCIENCE, INDUSTRIES, 2023)
The Albertine Rift has its basement rocks exposed near the surface from volcanic and plate tectonics. Lidar and GPR can be mounted on drones, automated vehicles, and airplanes to aid in creating an action plan based on all the information collected. Satellites, with the recent Geospatial Upgrades (GEOINT), can help give directions on areas to explore and rising threat levels.
The canvassing will be able to identify populations of birds, plants, insects, and animals that are either endemic or threatened populations as we develop the zone.
FTP will have the mechanical abilities to engineer solutions on the spot. Jackhammers and drill attachments for mining drones and vehicles. Waiting for parts from a weak global supply chain will not cut the mustard—Seabee mentality, with an environmental twist, to help meet objectives. We can modify attachments for mining, medical, and any drone applications as needed. FTP will keep off-the-shelf solutions stocked, but we understand drone capabilities are expanding rapidly. (Nichols R. -3., 2021)
These labs will be in the center of the smart village, and the satellites will be on the fringes of the established perimeter to help expand the zone safely. This will enable a managed approach to help set achievable goals. FTP will initially expand in areas with the slightest threat landscape. Then, plans can be modified to address the threats through corrective measures to help secure compliance. The labs will be used as needed for medical analysis, experiments, cataloging, and other purposes.
Manned and UAV-EMT Units
FTP must safeguard workers and guests. FTP needs to be able to transport people with urgent medical needs, victims of disasters, and other circumstances quickly. Helicopters, ground units, and UAV-EMT units will coordinate the EMT units. Most will be gas-powered, quad-engine drones, and others will be electric. An infrastructure needs to be built to handle air mobility for electric drones and vehicles. Foldable or portable stretchers will be at mining and other locations in the development zones. They would be easy to design. Forward units can call ahead for the UAV EMT unit to come to the area. They would do triage, put the person on a stretcher, and potentially more prep according to training. The person at the location must be trained in triage and medical evacuation standards. Then, four handles to help load a patient into the transport. Blunt force trauma and paralysis are a concern, and that’s why an SOP will be developed to mitigate too much movement of patients.
This can be used to rescue people trapped by flooding. They are lowering down a safety vest and lanyard for evacuation to help people trapped in houses, cars, and other places. South Africa would be a tremendous urban testing area. Johannesburg and Pretoria would have active mining operations in the area. The manned and UAV-EMT units will fly in and out of metropolitan hospitals. Valuable urban air mobility data will be collected. Initially, FTP would be using heliports. Then, FTP can modify the concept to fit the Smart Village into a Smart City medical location plan. Separate locations throughout the city are available depending on the emergency or medical treatment needed. This will cut down on air traffic to one central location. Spreading out medical facilities will quicken patient treatment. FTP would need infrastructure built and secured zones to do it in. Regulatory compliance would also need to be addressed in South Africa, Zimbabwe, DRC, and other locations. It would be an economic development zone, so FTP would require local, country, and global compliance for this to work. (Nichols R. -3., 2021)
Lake Kivu-UUV-Energy
The pressures at the bottom of Lake Kivu and different layers of gas are a data gold mine. Energy is on everyone’s mind, but the dangerous trapped gases need scientists to develop the resource. A company has a floating platform for methane extraction but does not understand all of the ramifications of extraction. During the recent earthquakes, all operations should have been temporarily suspended. It didn’t happen because of financial and energy concerns. [6] Suspending operations would have severe consequences for Rwanda: Kivu Watt produces around 30 percent of the annual electricity consumed in the East African nation. (AFRICANEWS, 2021)
Lake Kivu can simulate some of the conditions of space travel. The extreme pressures at the bottom of the Lake, coupled with the layers of water and gas, can yield important data that will help keep the population safe around the Lake. Propellants used in UUVs can break through the CO2 and Methane layers. It is a data goldmine. FTP will be able to source direct concentration levels and quantities of gas information. At the same time, the extreme pressure, salinity, and gas cavities would be similar to the data one can get on the Moon of Europa. It would be an extreme test for sensors, engines, and other equipment.
By studying Lake Kivu, scientists could create gigantic natural batteries out of other lakes in specific locations. Can the natural energy-building effects of the Lake be recreated? That area is a carbon trap, and having a UUV will help study the water coming out of the natural springs. Placing sensors at the inlets will give exact information about the chemical composition that makes the CO2, then Methane. Sensors should be placed at different layers to understand further how energy is created. When we travel to other planets, this information will be helpful in generating power as needed.
The Lake is between the DRC and Rwanda, and both have some claims to this energy. The countries have some working agreements between them, and considerations will have to be made as the DRC looks to start developing the methane as well. The potential to work together on bigger goals, like energy independence, can help foster lasting cooperation if developed as a whole. The peat bogs of the DRC and the Republic of the Congo hold excellent energy potential. European countries are utilizing peat for multiple purposes.
Africa has water. All you need is peat bricks to start generating electricity at the factory level or put it into an electrical grid. FTP can build the grid differently than America by allowing steam, solar, wind, and other energy sources to be placed directly into the grid or city energy station. Build it right the first time. Steam-electric power stations will help achieve goals for now and the future. When pressurized and made into a brick and then made into charcoal, it can be used in steelmaking.

Conclusions
We need to Feed The Planet through advanced farming technologies for humanity. The Feed the Planet project envisions a high-tech organic farming solution. This project’s grains, vegetables, and fruits can feed a reasonable population! Africa’s land mass size is incredible. Planners are just starting to grasp its full potential. The abundant resources will help enrich people and help others with basic needs. Producing vast amounts of organic food will help lower food costs globally. FTP will provide a canvas with different locations to paint a picture to end food scarcity issues globally.
We can engineer solutions for water scarcity issues. Depending on the area, we can drill for deep water aquifers, harvest rainwater, desalination of ocean water, and reverse osmosis techniques, to name a few. Salty water from storm surges is making healthy water unusable in some areas. The technology exists to build plants powered by solar or other energy options easily. Feeding the Planet is a step in the right direction. It is a project for the future of humanity.
Recommendation
FTP needs a sponsor for a lab-scale unit to prove the concept of operations. [7]
References
AFRICANEWS. (2021, 1 20). in-rwanda-kivuwatt-transforms-gas-from-killer-lake-into-electricity. Retrieved from https://www.africanews.com/: https://www.africanews.com/2022/01/20/in-rwanda-kivuwatt-transforms-gas-from-killer-lake-into-electricity/
Atkinson, J., & al., e. (2009). Natural Ventilation for Infection Control in Health-Care Settings. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK143277/#:~:text=What%20is%20natural%20ventilation%3F,wind%20towers%20and%20trickle%20ventilators
DATA SCIENCE, INDUSTRIES. (2023, 3 23). the-benefits-of-geospatial-data-for-mining-operations. Retrieved from https://picterra.ch/blog/: https://picterra.ch/blog/the-benefits-of-geospatial-data-for-mining-operations/#:~:text=Increased%20safety%20and%20risk%20management,for%20a%20safer%20working%20environment
DeMaio, C. D. (2024, June 15). Discussion about Militia Activities (UNCLASSIFIED) in Itombwe Mountains. (S. P. Nichols, Interviewer)
Facilitator, C. (2021, May 13). Smart City – Elements, Features, Technology and Govt. Approach. Retrieved from https://constrofacilitator.com/: https://constrofacilitator.com/smart-city-elements-features-technology-and-govt-approach/
Gearino, D. (2022, June 30). inside-clean-energy-broccoli-solar-agrivoltaics. Retrieved from https://insideclimatenews.org/: https://insideclimatenews.org/news/30062022/inside-clean-energy-broccoli-solar-agrivoltaics/
Gupta, D. &. (2020). Smart-and-Connected-Supply-Chain-Management-Scenario_fig4_343124947. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Smart-and-Connected-Supply-Chain-Management-Scenario_fig4_343124947
Knaple, B. (n.d.). Figure 12-1 Hanging Gardens of Africa Sketch for Feed the Planet. Advanced Technologies for Humanity. KSU, Manhattan, KS.
Knaple, B. (n.d.). Figure 12-3: Artist rendering Vertical Solar and Wind. Advanced Technologies for Humanity. KSU, Manhattan, KS.
Mirani, K. (2018, Jan 11). The-hanging-garden. Retrieved from https://kitaghana.dudaone.com/: https://kitaghana.dudaone.com/the-hanging-garden
Nichols, R. -2. (2022). Drone Delivery of CBNRECy DEW Weapons: Emerging Threats of Mini-Weapons of Mass Destruction and Disruption. (WMDD). Manahattan, KS: https://newprairiepress.org/ebooks/46/.
Nichols, R. -3. (2021). Disruptive Technologies with Applications in Airline, Marine, and Defense Industries (2021). Manhattan, KS: https://newprairiepress.org/ebooks/38/.
Nichols, R., & al., e. (2019). Unmanned Aircraft Systems in Cyber Domain: Protecting USA’s Advanced Air Assets, 2nd Edition. Manhattan, KS: https://www.newprairiepress.org/ebooks/27.
Odero, C. (2021, 12 7). science-technology-parks-are-key-to-leapfrogging-africas-economic-growth. Retrieved from https://cioafrica.co/: https://cioafrica.co/science-technology-parks-are-key-to-leapfrogging-africas-economic-growth/
Photograph by Robin Hammond, N. G. (2024, Jan 18). africa-lake-kivu-explosion-energy (Article by Deena Mousa). Retrieved from https://www.nationalgeographic.com/: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/africa-lake-kivu-explosion-energy
Powell, C. S. (2019, 2 28). 30-million-page-library-heading-moon-help-preserve-human-civilization. Retrieved from https://www.nbcnews.com/mach/science/: https://www.nbcnews.com/mach/science/30-million-page-library-heading-moon-help-preserve-human-civilization-ncna977786
UN: Department of Economic and Social Affairs- Sustainable Development. (2024, June 29). Feed the Planet. Retrieved from https://sdgs.un.org/partnerships/: https://sdgs.un.org/partnerships/feed-planet
UNICEF. (2024). school-box-guidelines-use. Retrieved from https://www.unicef.org/: https://www.unicef.org/supply/documents/school-box-guidelines-use
Wikipedia. (2024, 6 26). Cuvette_Centrale. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cuvette_Centrale
Wikipedia. (2024, 6 26). PEAT. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peat
End Notes
[1] “The Kumasi Institute of Tropical Agriculture (KITA) is a non-profit premier tropical agricultural college in Ghana. We network with local and global institutions to better the lives of rural farmers, unemployed youth, hungry and homeless families, women, people living with AIDS and orphans, needy street children, the aged, and the disabled. This is done through training, seminars and workshops, technology transfers, on-farm research, environmental conservation, volunteer exchange, seeds and food aid, input and clothing distribution, and children’s sponsorship. This has contributed to environmentally sustainable development that enhances the local economy, the nation, and the quality of life in Africa since 1984.” (Mirani, 2018)
[2] “Feed the Planet was founded by Worldchefs in 2012 as a way to empower and mobilize our global chefs’ network passionate about building a better future. We’re committed to using our voices to help ensure a more equitable and sustainable food system for all.” “With five active global programs, Feed the Planet directly contributes to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals by providing professional culinary education and employment to vulnerable populations (Like a Chef), encouraging children and young adults to adopt sustainable eating habits (Food Heroes Challenge and RePlate), helping food services reduce food waste (Food Waste Challenge) and educating culinary professionals on sustainable culinary practices (Sustainability Education for Culinary Professionals).” (UN: Department of Economic and Social Affairs- Sustainable Development, 2024) In 2016, Worldchefs joined forces with Electrolux Food Foundation and AIESEC, the world’s largest youth-led organization. Since that time, Feed the Planet has grown into a dynamic, collaborative effort for inspiring social change.”
[3] According to USAFRICACOM, the Itombwe Mountains, which are ripe for organic farming, are also heavily infested with unfriendly militia. (DeMaio, 2024)
[4] DRC – Democratic Republic of Congo
[5] PEAT: Quote: “Peat accumulates partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. Sphagnum moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most common components of peat, although many other plants can contribute. The biological features of sphagnum mosses act to create a habitat aiding peat formation, a phenomenon termed ‘habitat manipulation.’ Soil primarily consists of peat and is known as histosols. Peat forms in wetland conditions, where flooding or stagnant water obstructs oxygen flow from the atmosphere, slowing the decomposition rate. Peat properties such as organic matter content and saturated hydraulic conductivity can exhibit high spatial heterogeneity. Peatlands, particularly bogs, are the primary source of peat; although less common, other wetlands, including fens, pocosins, and peat swamp forests, also deposit peat. Landscapes covered in peat are home to specific plants, including Sphagnum moss, ericaceous shrubs, and sedges. Because organic matter accumulates over thousands of years, peat deposits provide records of past vegetation and climate by preserving plant remains, such as pollen. This allows the reconstruction of past environments and the study of land-use changes.” [Additional live links disabled. See Wikipedia for more information.] (Wikipedia, 2024)
[6] Author conjecture.
[7] Further information on FTP is available from the chapter author.
[8] Figure 12-1: Source: (Knaple, Figure 12-1: Hanging Gardens of Africa Sketch by author for Feed the Planet)
[9] Figure 12-3: Source: (Knaple, Figure 12-3: Artist rendering Vertical Solar and Wind)

