1 La riqueza de la música hispana – Yasmin Gavigan
La riqueza de la música hispana
This lesson is intended to show the Spanish learners at the intermediate level the richness of Hispanic music and expand their knowledge beyond the most common music genres such as Salsa and Reggaeton.
Learners Level
This activity is designed for Spanish learners at the Intermediate Mid/High level who have taken the equivalent of at least 3 semesters at the colleague level.
Modality
The activities in this lesson can be adapted for an in-person course that uses the Flip-Classroom approach, or for a synchronous or asynchronous online course.
Learning Objectives
At the end of the unit, students will be able to:
- Recognize the Hispanic music genre already known
- Learn about the Hispanic music in general
- Discuss your favorite music genre and/or singers
- Listen to identify 4 – 5 different Hispanic music genres
- Learn the origin, history, importance, and representative artists of different Hispanic music genres
- Recognize by listening to different Hispanic music genres
- Select one of the genres studied in the lesson and write a blog
- explaining their opinions about it using expressions with subjunctive
- providing recommendations to promote this particular genre
Antes de empezar
1. ¿Cuáles géneros musicales hispanos conoces o has escuchado?
2. Lectura. Lee con atención la siguiente lectura sobre un breve recorrido por la historia de la música hispana.
 La música hispana: una mezcla de culturas
La música hispana: una mezcla de culturas
¿Qué es la música hispana para ti? Muy probablemente pienses en géneros como la salsa y el reggaetón, así como en artistas crossover como Bad Bunny, JBalvin, Shakira, Selena entre otros. Sin embargo, la música hispana abarca una variedad de estilos musicales de España y América Latina, cuyos géneros son una mezcla de culturas. En España, por ejemplo, el flamenco, de origen principalmente árabe, es uno de los bailes tradicionales, mientras que en Latinoamérica se observa un sincretismo de elementos europeos, indígenas y africanos.
En cuanto a Latinoamérica, antes de la llegada de los españoles la música indígena se caracterizaba por el uso de instrumentos hechos de materiales naturales como cañas, conchas, carcazas de animales y troncos huecos para crear instruments como el charango, la zampoña, la maracas, el güiro, el bombo, etc. Hoy en día, muchos pueblos indígenas y países con un alto porcentaje de población indígena, como Ecuador, Perú y Bolivia, aún conservan sus instrumentos y músicas autóctonas. Un ejemplo de esto es la música andina. Con la llegada de los españoles, se incorporaron elementos europeos como la guitarra y la lírica o poética española creándose así una fusión de nuevos ritmos.
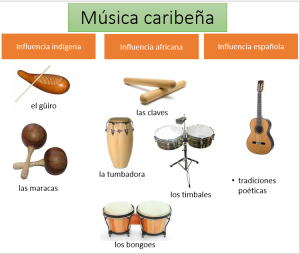 Posteriormente, en especial en el Caribe, con la llegada de los esclavos africanos se adoptaron los instrumentos de percusión como la clave y una variedad de tambores que se transformaron en batá, bongoes, congas, timbales y tumbadoras. Gracias a la percusión africana, la música caribeña está asociada al baile y cada ritmo posee su propio baile, como es le caso del son, la rumba y el chachachá cubanos; el merengue dominicano; la cumbia colombo-panameña; la plena puertorriqueña; entre otros.
Posteriormente, en especial en el Caribe, con la llegada de los esclavos africanos se adoptaron los instrumentos de percusión como la clave y una variedad de tambores que se transformaron en batá, bongoes, congas, timbales y tumbadoras. Gracias a la percusión africana, la música caribeña está asociada al baile y cada ritmo posee su propio baile, como es le caso del son, la rumba y el chachachá cubanos; el merengue dominicano; la cumbia colombo-panameña; la plena puertorriqueña; entre otros.
La música hispana es tan rica y variada en ritmos y géneros musicales que cada país tiene una infinidad de músicas (Colombia tiene más de 130 ritmos diferentes, por citar solo un ejemplo), producto de nuevos contactos culturales. Dicha hibridación cultural continúa hoy en día y gracias a ella, géneros como el vallenato colombiano, el hip hop caribeño, el Tropipop, la música norteña, entre otros, se han internacionalizado.
A Reconocer algunos géneros hispanos
Para recordar
Con base en la lectura de la section Antes de empezar y la información que leíste sobre el tropipop, la bachata, el vallenato y la champeta, comprueba qué tanto aprendiste contestando las siguientes preguntas.
A Reflexionar
Contesta las siguientes dos preguntas en tu cuaderno y prepárate para compartir tus respuestas en la discusión en clase (ya sea asincrónica o sincrónica).
- De los géneros que escuchaste hoy, ¿cuál te llamó más la atención y por qué (puedes mencionar aspectos como el ritmo, el baile, su historia, importancia, etc.)?
Elabora tu respuesta con bastantes detalles y usa expresiones como: es importante que…, me pareció interesante que…, no pienso/no creo que…para expresar tus opiniones sobre este género. ¡Ojo! con el uso del subjuntivo. - Por último, escribe 2 – 3 oraciones para recomendar este género a tus amigos y compañeros de clase. Usas expresiones como: recomiendo que…, sugiero que…, te aconsejo que…, es bueno/importante/necesario/etc. que… ¡Ojo! con el uso del subjuntivo.
¡Eso es todo!
Espero que hayas aprendido a identificar las diferencias entre los géneros musicales hispanos discutidos en esta lección y aprendido algo sobre su historia e importancia.

Tips and Instructions for Instructors Using this Resource
This lesson could serve as an introductory preparatory activity for in-class discussions aimed at introducing various Hispanic music genres. If used in this manner, the instructor could employ the “A reflexionar” questions as a warm-up activity in both in-person and online courses (whether asynchronous or synchronous). Another potential warm-up could involve conducting a quick survey to determine the most popular genre among the students.
During the class session, the instructor could introduce 4-5 genres (e.g., Tango, Musica andina, merengue, música romántica, rock en español, etc.) following a consistent format: presenting a song or music video representing a specific genre, prompting students to guess the genre, and then providing a brief informative presentation about that genre. As a concluding activity, students could discuss their favorite genre learned thus far. Additionally, each student could select a song from their favorite genre discussed in class and prepare a creative activity to present it to the class. Alternatively, students could create promotional ads to persuade their classmates to listen to a song or artist from their preferred genre.
Given that one of the lesson’s objectives is for students to recognize different music genres when they hear a song, instructors could curate a playlist on YouTube or Spotify and play songs in class, prompting students to identify the genre.
This lesson offers great versatility, allowing instructors to adapt it to their teaching style, course format, and the characteristics of their students.
Creada por Yasmin Gavigan, Kansas State University 2024
I am a native Spanish speaker from Bogotá, Colombia. I have a Master’s in Second Language Acquisition from Kansas State University. I have taught Spanish language courses at both basic and intermediate levels (SPAN 1 – 4; SPAN 410 – Spanish Communication through Pop Culture) at Kansas State University. As an educator, I am dedicated to guiding my students to actively engage with the course content through activities that foster personal connections, application to their daily lives, and interaction with others and the world around them. I advocate for learning through interactive, hands-on classroom activities that encourage critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and an appreciation for their culture and others. I aspire for the skills they acquire in my class to contribute to their personal, intellectual, and professional growth as they transition from the classroom to real-world contexts.
My research interests encompass second language acquisition, bilingualism, Spanish heritage learners, online learning, and advising methodologies.


